Interest Rate Risk at Regional Banks & the Formation of a "Balance Sheet Management Consortium"

In a January 2025 report, the Nikko Research Center analyzed the public disclosures of 99 regional banks - 10 internationally operating banks, 53 regional banks excluding the internationally operating banks, and 36 second-tier regional banks.
Under various interest rate scenarios, the change in value of securities, loans, deposits, etc. was calculated. The maximum loss across these scenarios is taken as ∆EVE (change in economic value). The scenarios for the change in the yield curve are based on internationally unified standards, including up/down parallel shifts and steepening of the yield curve.
The materiality test ratio is calculated by dividing ∆EVE by the amount of capital (Tier 1 capital for internationally operating banks), resulting in a numerical value that indicates the percentage of equity capital that is accounted for by changes in economic value due to interest rate fluctuations.
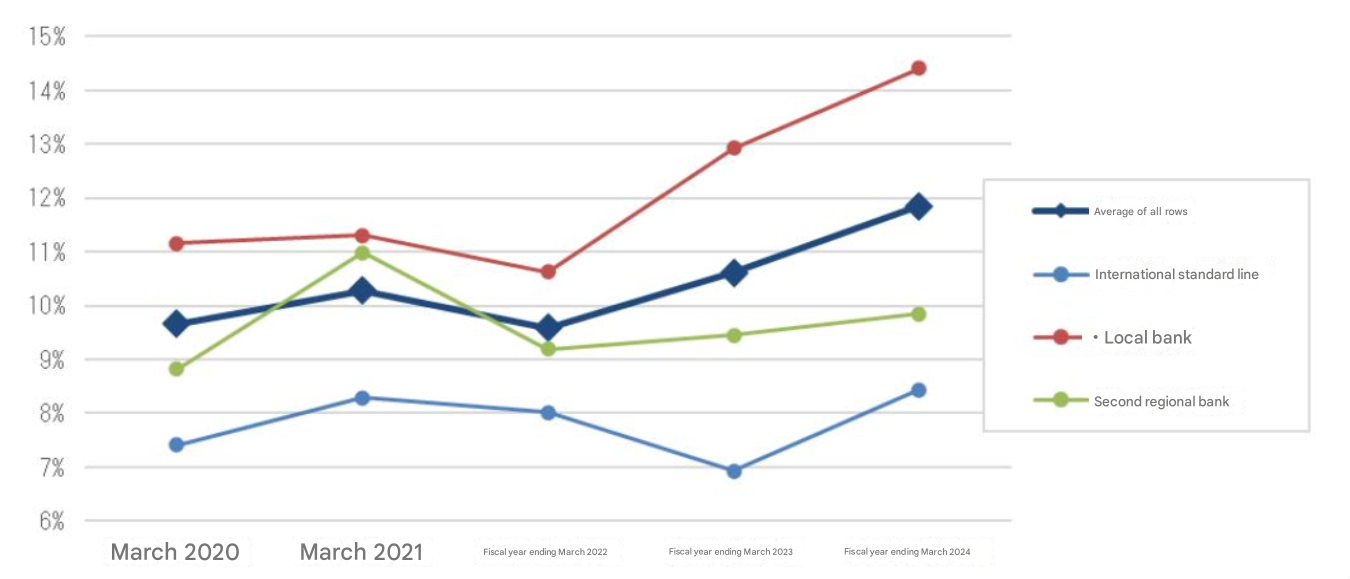
The graph shows the materiality test ratio for all banks and the weighted average by type of business for the five fiscal years from the fiscal year ended March 2020. For all but second-tier regional banks, the test ratio is the highest since disclosures of interest rate risk in the banking book were implemented for domestic banks. Naturally, the weighted averages do not show the distribution.
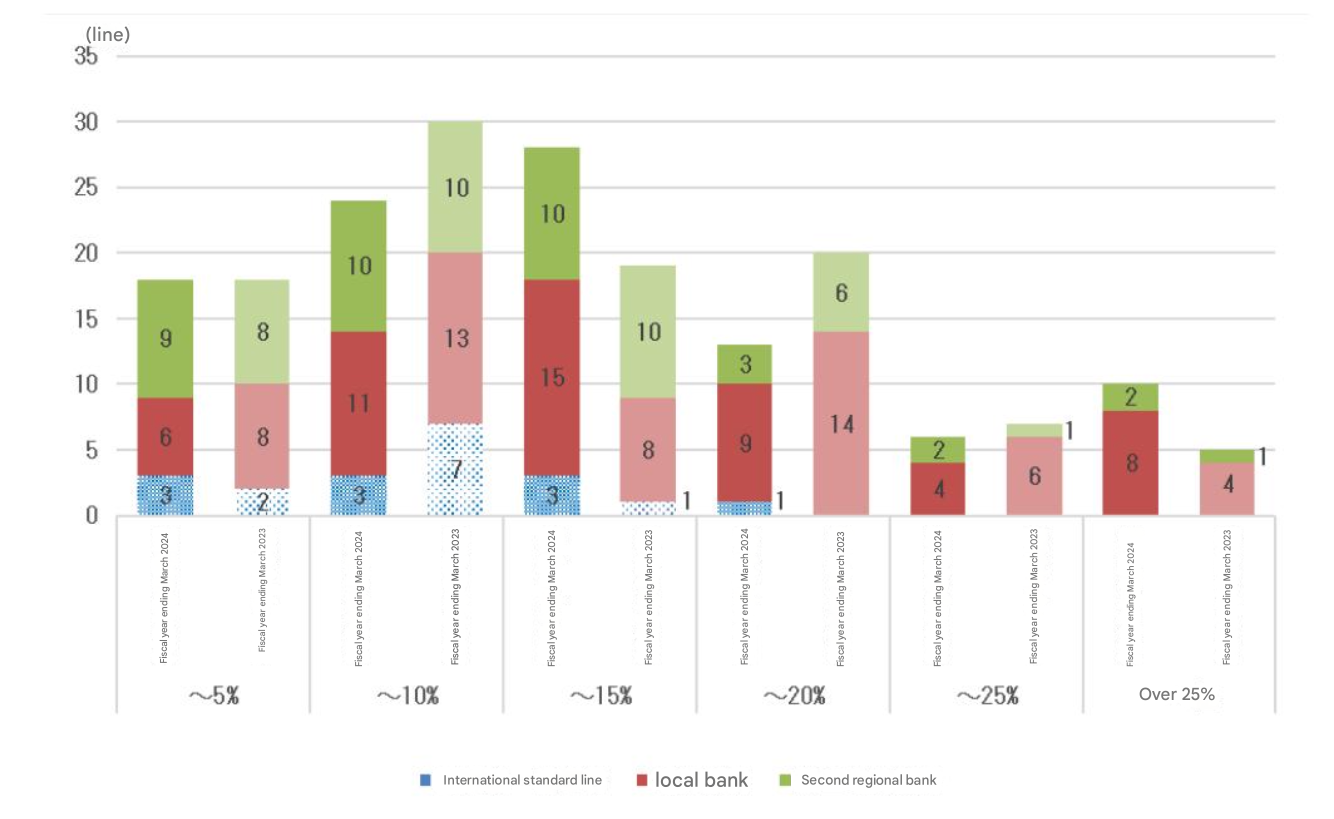
In the fiscal year ending March 2023, 12 banks had a materiality test ratio that exceeded the 20% threshold for domestic standard banks. The number of banks with a ratio of over 25% increased to 10 during the fiscal year ending March 2024, doubling from five in the previous fiscal year.
In addition, the most common level was the 5% to 10% range for the period ending March 2023, but this changed to the 10% to 15% range in the period ending March 2024.
The threshold for internationally-accelerated banks is 15%, which is stricter than that for domestic banks. However, only one out of 10 internationally operating banks exceeds this threshold.
In light of further expected normalization of the Bank of Japan's monetary policy, and associated policy rate increases, this level of interest rate risk in the regional banks' banking book has the Financial Services Agency worries, which is apparently implementing a closer supervision mechanism.
Establishment of "Balance Sheet Management Consortium"
With the above as background, Shizuoka Bank has launched a private sector initiative. It is working to enhance its "core deposit model" to achieve stable funding income and improve the soundness of asset-liability management (ALM) as part of its commitment to "balancing social value creation and corporate value enhancement" in the Group's medium-term management plan.
Shizuoka Bank has now established the "Balance Sheet Management Consortium" aimed at advancing ALM in collaboration with Allianz Global Investors Japan (Allianz GI) and NS Financial Management Consulting (NSFMC).
Background and Purpose of Establishment
With the arrival of a "world with interest rates" following the Bank of Japan's policy rate increases, Shizuoka Bank introduced a "new core deposit model" in September 2024 to fulfill its role as regional financial infrastructure that provides smooth funding supply under any circumstances, and has been working to measure the economic value of core deposits.
This model was introduced through joint research with Allianz GI, NSFMC, and Professor Masaaki Kijima from Shunan University. It is an advanced model that can estimate future deposit balances by incorporating individual parameters such as interest rate environment trends (rising/falling), seasonal factors, and inter-segment correlations into monthly deposit balance fluctuation rates.
Shizuoka Bank has now decided to further develop this initiative by establishing a "consortium" that aims to advance asset-liability analysis and evaluation centered on the core deposit model, and strengthen risk management systems against interest rate increases and other factors.
Going forward, Shizuoka Bank will recruit regional financial institutions to participate in this consortium, deepen discussions on balance sheet management that considers changes in external environment such as "a world with interest rates" and "population decline," and work toward further advancement of ALM by understanding risk tolerance in each bank's balance sheet and improving risk-return profiles.
Key Consortium Members and Their Roles
- Shizuoka Bank and other regional financial institutions: Provide data on deposit trends and expertise as regional banks
- Allianz GI: As an asset management company with bases in Germany and countries worldwide as part of Europe's largest insurance group, their Risk Lab department, which has academic networks with institutions such as the Technical University of Munich, provides expertise on overseas cases and other knowledge
- Masaaki Kijima (Advisor): Creator of the original core deposit model prototype, providing support from an academic perspective
- NSFMC: As a member of the Nippon Steel Solutions Group, a major systems integrator, provides expertise in core deposit model development and data science




