Policy Briefing: The Artificial Intelligence Basic Plan

Japan's new AI Basic Plan, released as a draft on December 19, is framed as a national "counteroffensive" designed to reverse a perceived lag in artificial intelligence investment and utilization. The strategy directly confronts long-standing domestic challenges—including population decline, labor shortages, and stagnant wages—by positioning AI as a core engine for economic and social revitalization. Acknowledging that it has fallen behind global competitors, Japan recognizes that the global competitive landscape for AI is shifting. The market is beginning to evaluate the creation of specific, high-value applications more than the sheer scale of investment in foundation models, presenting a critical opportunity.
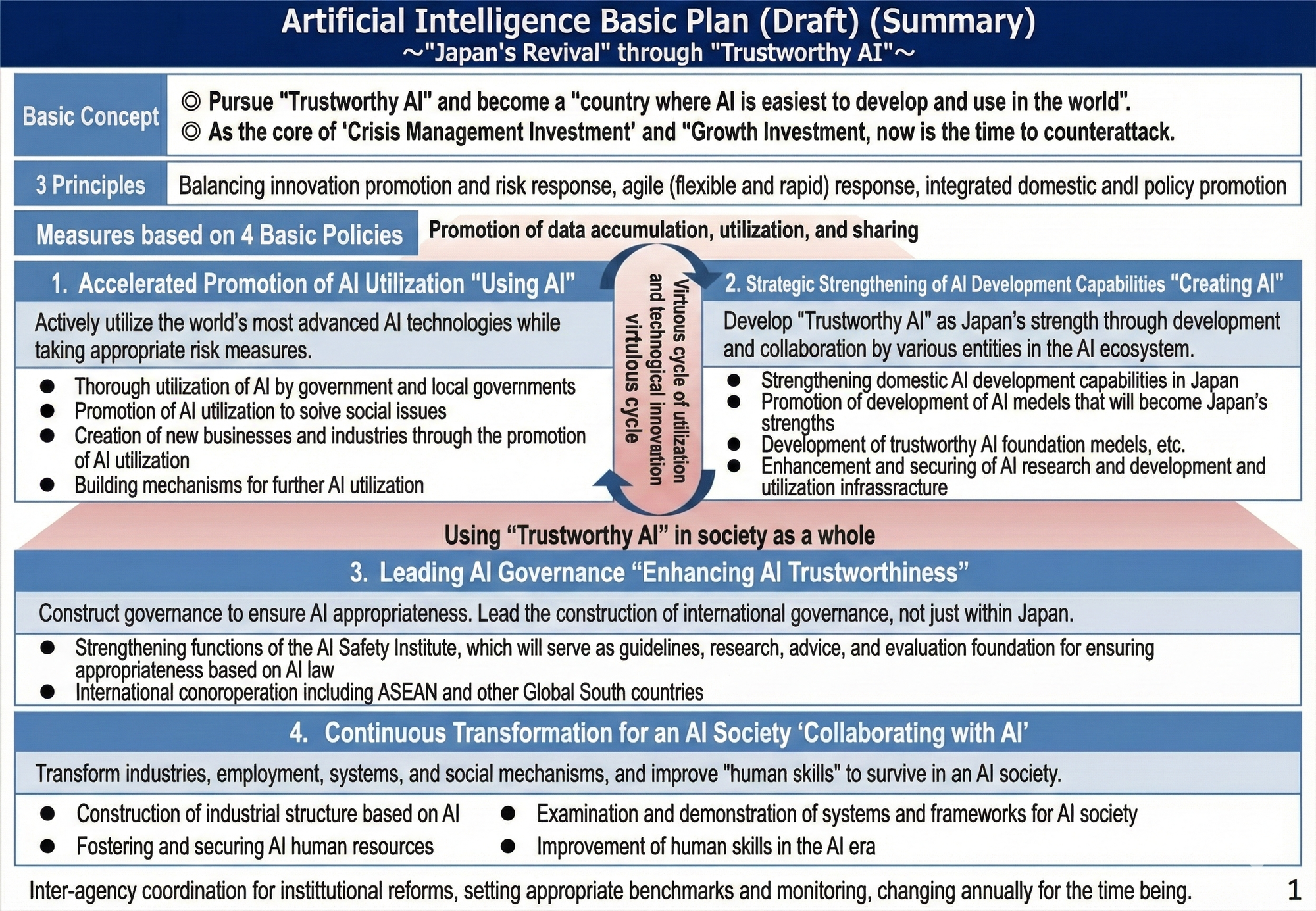
At the heart of this counteroffensive is the concept of "Trustworthy AI" (信頼できるAI). This is not merely a branding exercise but a direct strategic response to the evolving market. The plan leverages Japan's global reputation for quality and reliability to forge a competitive advantage in high-trust AI applications. Rather than competing on raw capital, Japan aims to lead by creating safe, secure, and transparent AI systems tailored to its robust industrial base, thereby accelerating domestic adoption and generating a virtuous cycle of development and implementation.
This entire strategy is driven by a clear and ambitious national vision: to become "the easiest country in the world to develop and utilize AI." This goal serves as the guiding star for all subsequent policies, aiming to create an environment where government, industry, and citizens can confidently embrace AI. To achieve this vision, the plan is anchored in a set of foundational principles that guide its implementation.
1. Foundational Principles of Japan's AI Framework
To realize its ambitious national goal, Japan's AI strategy is built upon three core, non-negotiable principles. These principles collectively create a framework designed for both domestic confidence-building and international alliance-building. By establishing a clear and stable foundation for all policy actions, Japan seeks to assure stakeholders that its approach to AI is coherent, predictable, and aligned with a human-centric vision. The strategic integration of agile governance with risk management represents Japan's answer to the global debate on how to regulate AI without stifling innovation.
- Balancing Innovation Promotion and Risk Response (イノベーション促進とリスク対応の両立): This principle commits the government to simultaneously fostering rapid technological advancement while methodically addressing AI-related risks. It seeks to unlock AI's potential for growth while ensuring safety, security, and public trust by managing challenges such as misinformation, algorithmic bias, and privacy infringement.
- Agile Response (アジャイルな対応): Recognizing the rapid pace of technological change, this principle establishes a flexible and adaptive governance model. Japan will employ a continuous PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle to evaluate outcomes and adjust policies quickly, ensuring that its strategic framework remains relevant and effective in a fast-evolving AI landscape.
- Integrated Domestic and Foreign Policy (内外一体での政策推進): This principle mandates a unified approach where domestic AI policies and international diplomatic strategies are designed to be mutually reinforcing. By aligning its internal development goals with its external engagement, Japan aims to position itself as a key node in the global AI ecosystem.
These guiding principles form the bedrock of the strategy, informing the four concrete policy pillars that constitute the national action plan.
2. The Four Pillars of the National AI Action Plan
Translating its high-level principles into practice, Japan's AI strategy is organized around four fundamental policy pillars. These pillars create a comprehensive action plan covering the full lifecycle of AI innovation—from widespread utilization and strategic creation to robust governance and proactive societal adaptation.
2.1 Pillar #1: Accelerating AI Utilization ("Using AI")
This pillar is designed to cultivate a society where AI is proactively used by all citizens and organizations to solve problems, enhance productivity, and drive innovation. To lead by example, the government will be a first mover in adopting AI to improve public services.
- Government-Led Adoption: Promoting the use of "Government AI" with the goal for all central government employees to utilize it to improve the quality and efficiency of administrative services. To ensure top-down commitment, management-level staff (指定職・管理職) will be expected to lead by example.
- Solving National Challenges: Actively supporting AI implementation in critical sectors facing significant challenges, including healthcare and elder care, disaster prevention, infrastructure management, and national security.
- Data Infrastructure: Promoting the secure sharing of high-quality data across organizations to create the rich datasets needed for high-performance AI, with a focus on sectors where Japan holds a competitive advantage.
2.2 Pillar #2: Strategic Enhancement of AI Development ("Creating AI")
This pillar aims to build a self-sufficient and globally competitive domestic AI ecosystem, spanning from foundational infrastructure to specialized applications. The goal is to secure Japan's technological autonomy and bolster its national and economic security in an era of intense global competition.
- Targeted R&D Investment: Concentrating public and private investment in Japan's identified "winning" areas, such as Physical AI (robotics, autonomous driving) and AI for Science, where the nation has strong industrial and research foundations.
- Infrastructure Reinforcement: Accelerating the strategic development of essential AI infrastructure, including domestic data centers, high-performance semiconductors, next-generation communication networks (Beyond 5G), and the stable power supply required to support them.
- Developing "Trustworthy AI" Models: Promoting the development of AI foundation models that reflect Japan's unique cultural and societal contexts, a goal supported by initiatives to create and expand high-quality Japanese language datasets.
2.3 Pillar #3: Leading AI Governance ("Enhancing AI Reliability")
The objective of this pillar is to establish a robust and agile governance framework that ensures AI is developed and used responsibly. This approach is built around a PDCA cycle for ensuring appropriateness at each stage of development, demonstration, evaluation, and operation. By enhancing AI's reliability, the plan seeks to build the public and corporate trust necessary to fuel a virtuous cycle of innovation and widespread adoption.
- Strengthening the AI Safety Institute (AISI): Drastically enhancing the AISI's capabilities for technical evaluation, risk assessment, and safety research to provide an empirical foundation for evidence-based policymaking.
- Combating Malicious Use: Developing and deploying effective countermeasures against the malicious use of AI, including AI-enabled cyberattacks, sophisticated fraud, and the proliferation of deepfakes and disinformation.
- International Leadership: Proactively leading international discussions on AI governance standards and norms, building upon the diplomatic foundation of the Hiroshima AI Process to foster global cooperation.
2.4 Pillar #4: Continuous Transformation for an AI Society ("Collaborating with AI")
This pillar focuses on proactively managing the profound societal shifts brought about by AI, ensuring that the transition is inclusive, equitable, and empowers citizens. The goal is to build a society where humans and AI can collaborate effectively to achieve shared prosperity.
- AI Talent Development and Reskilling: Implementing comprehensive measures for AI education from the primary school level upwards and creating robust national programs to support worker reskilling and adaptation to changes in the labor market.
- Systemic Reform: Reviewing and updating existing regulations and legal frameworks to ensure they are fit-for-purpose in an AI-integrated society, with a specific focus on critical areas such as intellectual property and civil liability (民事責任の所在や範囲).
- Enhancing "Human-centric" Skills: Promoting education that fosters uniquely human capabilities (人間力, ningen-ryoku) like creativity, critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication, ensuring that people are equipped to work alongside AI rather than be replaced by it.
While these four pillars define the scope of action, the plan's ultimate success rests on a sophisticated governance architecture designed to manage risk without sacrificing speed.
3. The Architecture of AI Governance and Risk Management
The centerpiece of Japan's strategy to deliver "Trustworthy AI" is a concrete, multi-layered governance architecture. This structure is intentionally designed to be both robust and agile, providing the stability needed to ensure safety and build confidence while maintaining the flexibility required to adapt to rapid technological innovation.
3.1 The AI Safety Institute (AISI) as the Technical Core
The AI Safety Institute (AISI) is positioned as the central technical body in Japan's governance framework. Its primary function is to conduct impartial, evidence-based technical evaluations of advanced AI models, assess their capabilities and potential risks, and provide the empirical data necessary to inform agile and effective policy.
To ensure the AISI can fulfill this critical role, the plan calls for its "drastic strengthening" (抜本的に強化). Two immediate actions are mandated to rapidly scale its capacity:
- The plan will immediately double its personnel.
- It will use the world-leading UK AI Safety Institute as a benchmark for its future scale and operational capabilities.
3.2 International Leadership through the Hiroshima AI Process
The Hiroshima AI Process serves as the cornerstone of Japan's international AI diplomacy. Launched during its G7 presidency, the process aims to build a global consensus among like-minded partners on the principles and practical policies needed to support safe, secure, and trustworthy AI.
Japan plans to continue leading this process and expand its global influence by creating a "Hiroshima AI Process Friends Group." This initiative is specifically designed to engage with a wider range of international partners, including key nations in ASEAN and the Global South. The strategic ambition is not merely to participate in global governance, but to position Japan as a central hub or "junction point" (結節点, kessetsuten) that connects different global AI ecosystems—such as those of the US, Europe, and the Global South—leveraging its "Trustworthy AI" brand as the basis for this interoperability.
This dual approach—building a strong domestic technical institution while simultaneously shaping global norms—forms the foundation of Japan's strategy to lead in the age of AI.
4. Conclusion: A Unified Vision for National Revitalization and Global Leadership
Japan's AI Basic Plan is an integrated national strategy for what the government itself terms a "national rebirth" (日本再起, Nippon Saiki) through trustworthy AI. By framing its approach as a "counteroffensive," Japan signals a decisive commitment to harnessing AI to overcome its most pressing economic and demographic challenges. The central concept of "Trustworthy AI" serves as the unifying thread that connects the plan's ambitious economic, social, and diplomatic objectives, transforming a national reputation for reliability into a tangible competitive advantage. Ultimately, the plan charts a course toward a human-centric AI society, one that seeks to skillfully balance the pursuit of technological progress with the preservation of enduring human values.